Navigating Policy for Sustainable Honey Practices
Did you know that many wild plants and food crops need bees to pollinate them? This fact highlights how critical bee health and ecosystem sustainability are. Ethical beekeeping focuses on keeping bee colonies and their environments healthy. This is different from traditional methods that only care about how much honey is made. Ethical beekeepers use natural methods, harvest sustainably, and manage diseases well. They aim to lessen the harmful effects of large-scale industrial beekeeping.
Manukora is a good example of sustainable beekeeping. They place their hives in New Zealand’s remote forests. This gives bees a stable, natural home. It helps bees do well and leads to quality honey, all while keeping nature in balance. Manukora shows that caring for bee health and the environment is possible without sacrificing honey quality.
Key Takeaways
- Ethical beekeeping focuses on the well-being of bees and their ecosystems.
- Sustainable honey production policies are crucial for maintaining bee health.
- Natural approaches and sustainable harvesting techniques are central to ethical beekeeping.
- Examples like Manukora illustrate the benefits of prioritising ecological balance.
- Efficient disease management can mitigate the adverse effects of industrial practices on bee colonies.
Understanding Ethical Beekeeping
Entering the world of ethical beekeeping is essential. It focuses on bees’ health and the balance of their home ecosystems. This ensures bees get natural food and live in environments good for their welfare.
What Is Ethical Beekeeping?
Ethical beekeeping goes hand in hand with sustainability. It means doing as little harm as possible. This includes giving bees spaces that feel like their natural home. The goal is to boost honey bee colony health and not just make honey. By doing this, we help bees thrive and keep our environment healthy.
The Importance of Ethical Beekeeping
Why is ethical beekeeping crucial? Because it helps maintain biodiversity and protects bees, our top pollinators. Strong bee colonies are key for crops and ecosystems. They affect our food supply worldwide. By caring for honey bee colony health, we help secure a better future for bees and humans.
The Three Pillars of Ethical Beekeeping
Ethical beekeeping stands on three main pillars: outstanding Hive Management, sustainable harvesting, and controlling Honey Bee Diseases with organic methods. These rules focus on the well-being of bees and protecting their living spaces. This leads to stronger bee colonies and better-quality honey.
A Natural Approach
Being dedicated to natural methods is central to ethical beekeeping. It involves letting bees build their comb without too much human help. By doing this, it supports Organic Beekeeping. Bees can act naturally without the problems caused by man-made processes.
Sustainable Harvesting
Ethical beekeeping means only taking excess honey, ensuring bees have enough to eat. By doing so, especially when flowers aren’t blooming, keeps the bee colonies healthy and stable. This method puts the bees’ future first, not just making money.
Effective Disease Management
Using organic ways to manage bee diseases is key to ethical beekeeping. It avoids chemicals to safeguard bees and honey consumers. Using natural disease control strategies helps build strong, chemical-free environments for bees.
These ideas are the foundation of ethical beekeeping. They bring together great Hive Management, sustainable techniques, and Organic Beekeeping to keep bee communities thriving.
Impact of Industrial Beekeeping Practices
Industrial beekeeping has changed how we look after bees. A big worry is the drop in bee population linked to harsh methods. Unlike kinder beekeeping, industrial methods often care more about making more honey.
Harsh harvesting can take too much honey from hives. This forces beekeepers to use sugar water or corn syrup instead. But these don’t give bees the nutrients they need. It harms their ability to fight off sickness and breed properly.
Industrial beekeeping disrupts bees’ natural ways. The stress and bad diet from fake food makes them weak. This leaves them open to illness and stress from the environment. It adds to the serious issue of bee population decline.
Moving hives too often is another big problem. To get as much honey as possible, beekeepers move hives to different places. This stresses the bees and exposes them to more diseases and pests. It’s bad for bee colony sustenance.
We need to stop these harsh methods and follow kinder beekeeping ways. This is the only way to keep bee numbers up. We must do this to save these important pollinators for the future.
Promoting Biodiversity Through Ethical Beekeeping
Ethical beekeeping is all about helping local wildlife and bees. It uses ways to protect bee health and their homes. This keeps our ecosystem in balance. It means putting in native plants and making safe places for bees. This helps create strong, happy bee colonies.

The Role of Native Plants
Native plants are crucial for ethical beekeeping. They offer the right food for local bees. Putting nectar-rich plants in gardens gives bees food all season. I’ve seen how wildflowers and shrubs improve bee health and keep their numbers up.
Supporting Local Ecosystems
Bee-friendly gardening helps more than just bees. Ethical beekeepers make garden spaces that feel like natural homes. This not only helps bees but also other creatures and plants. Using wild spaces and planting different local plants makes healthy environments.
Ethical beekeeping also fights the problems caused by climate change. It does this by encouraging native plants in the UK. By planting and caring for these gardens, we help our local nature stay strong.
Avoiding Pesticides in Beekeeping
Stepping away from pesticides is key in ethical beekeeping. By avoiding chemicals, beekeepers boost Bee Health and make honey safer for everyone. This approach benefits not just the bees but also the environment and the people who enjoy honey.
Natural Pest Management Techniques
Choosing Chemical-Free Hive Management means using natural ways to control pests. This keeps harmful chemicals away from the hive. Methods like using predator insects or making the area less welcoming for mites protect bee colonies. And they do it without harming their health.
Benefits of Pesticide-Free Beekeeping
Opting for Organic Pest Control has many benefits. It lowers the chance of honey getting contaminated, ensuring a cleaner product. Such methods also protect the ecosystem’s balance, supporting Bee Health and the planet. This leads to better honey that doesn’t have synthetic chemicals in it.
| Aspect | Pesticide-Free Beekeeping | Conventional Beekeeping |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Use | None | Frequent |
| Bee Health | Enhanced | Often Compromised |
| Honey Quality | Purer | Potentially Contaminated |
| Environmental Impact | Sustainable | Harmful |
Policy and Regulation for Sustainable Honey
The sustainable honey sector relies on strong Honey Production Legislation. This legislation encourages beekeepers to follow eco-friendly practices. It includes the Bee Conservation Law for protecting bee habitats and promotes Sustainable Farming Practices.
To help bees and encourage Sustainable Farming Practices, lawmakers want to limit harmful pesticides. They support farming methods that are good for the environment. These steps are vital for a place where bees can live safely, away from dangerous chemicals.
- Restricting harmful pesticide usage to protect bee colonies.
- Promoting organic farming as part of Honey Production Legislation.
- Advocating for Bee Conservation Law to ensure habitat preservation.
Honey Production Legislation also aims to reward beekeepers who look after their bees and environment. By connecting policy with sustainable goals, we can help bee populations survive and thrive. They are key to agriculture all over the world.
Supporting Bee-Friendly Initiatives
The need for Pollinator Conservation is growing. It’s essential to join local and global efforts now more than ever. Doing so shares crucial information and sustainable ways to keep bee ecosystems healthy.
Local and Global Networks
Becoming part of Sustainable Beekeeping Networks makes a big difference. You can join at both local and international levels. Groups like the World Bee Project, Honey Bee Network, and International Honey Commission help a lot. They allow us to share knowledge and use sustainable methods to help bees thrive worldwide.
Participating in Conservation Programs
Taking part in Pollinator Conservation programs helps everyone. These efforts are led by organisations like the Xerces Society and Buglife. They focus on managing habitats and supporting bee populations. By working together, we aid in Bee Ecosystem Restoration and keep the environment balanced.
I believe joining these efforts teaches us much and allows us to help both bees and people. We all push towards a better ecosystem by being active in these groups and programs.
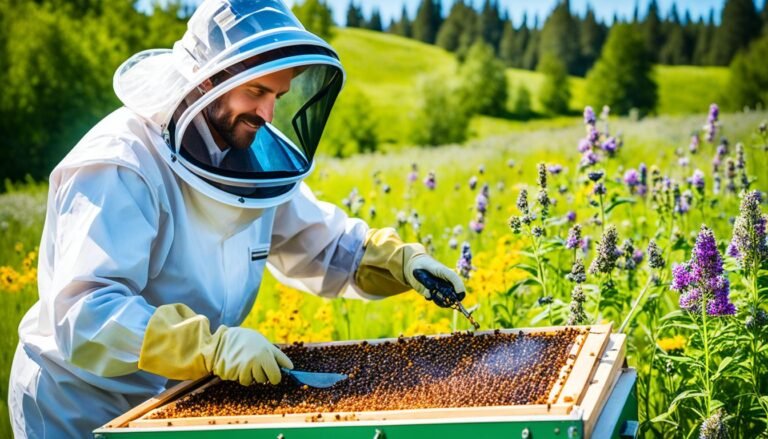
Best Practices for Harvesting and Processing Honey
In ethical beekeeping, how we harvest and process honey is important. It affects the honey’s quality and the bees’ wellbeing. Using sustainable methods means we take honey responsibly. We also keep its natural goodness, making it nutritious and real.
Harvesting Techniques
When to harvest honey is key; we must wait until it’s fully ripe. This means the honey is rich in nutrients. Using gentle methods to extract it, like a soft brush or mild smoke, keeps the bees calm. These ways help the bees stay healthy and behave naturally.
Processing Methods
Handling honey with care after harvesting keeps its health benefits. Not using too much heat is important because heat can harm its enzymes and antioxidants. Storing honey correctly in sealed glass jars keeps it pure and fresh. Clear labels on jars tell consumers the honey is ethically made and natural. This builds trust.
Following these practices helps bees stay healthy and gives us pure honey. This is good for bees, their surroundings, and us. It lets everyone enjoy honey that is both tasty and made the right way.








 Wildflower Honey
Wildflower Honey